Persistent identifiers
Overview
Teaching: 40 min
Exercises: 10 minQuestions
What is a persistant identifiers?
What is the structure of identifiers?
Why it is important for your dataset to have an identifiers?
Objectives
Explain the definition and importance of using identifiers
Illustrate what are the persistent identifiers
Give examples of the structure of persistent identifiers
Persistent identifiers
Identifiers are a long-lasting references to a digital resources such as datasets, metadata .. etc. They provide the information required to reliably identify, verify and locate your research data. Commonly, a persistent identifier is a unique record ID in a database, or a unique URL that takes a researcher to the data in question, in a database.
That resource might be a publication, dataset, or person. Persistent identifiers have to be unique, globally only your data are identified by this ID that is never used by anyone in the whole world. In addition, these IDs and must not do not become invalid over time. Watch our RDMbBites on the persistent identifiers to understand more.
Identifiers are very important concept of the FAIR principle. They are considered one of the pillars for the FAIR principles. It makes your data more Findable (F)
It is important to note that when you upload your data to a public repository, the repository will create this ID for you automatically.
Based on how to FAIR, there are many resources that can help you know which databases will assign PID to your data. One of these resources is FAIR sharing, it provides you with a list of databases grouped by domains and organizations.
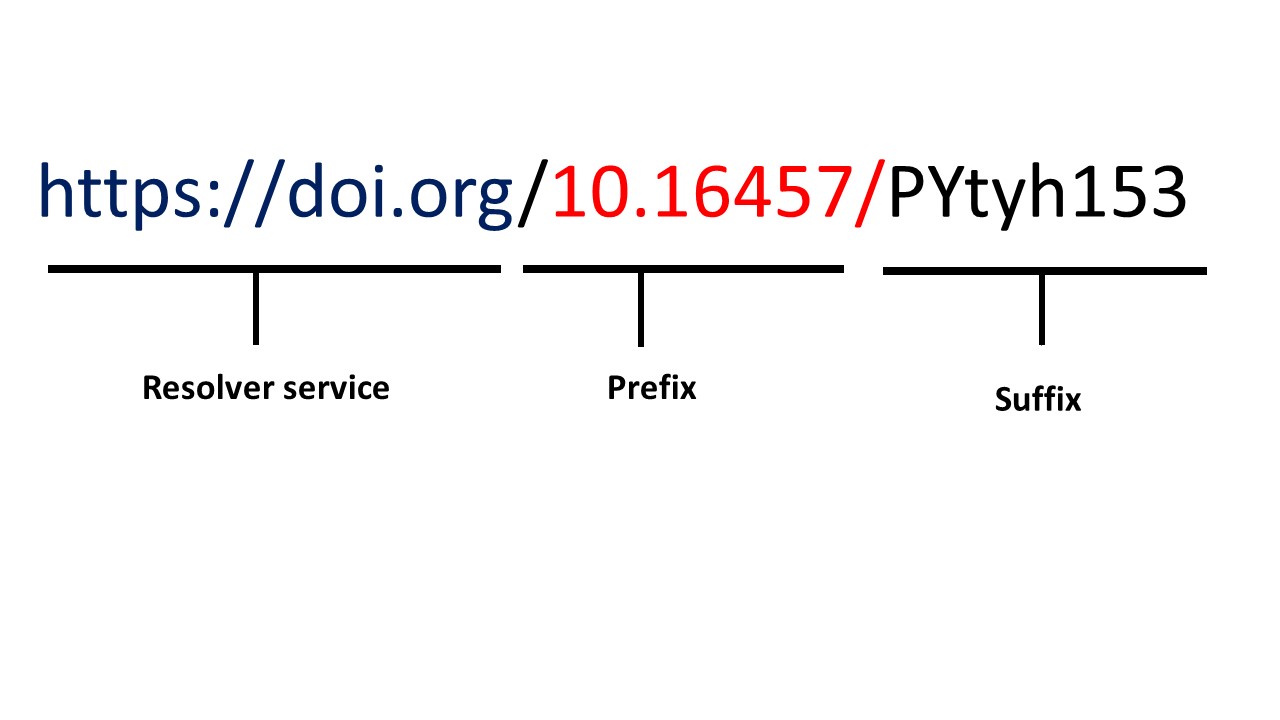
The Structure of persistent identifiers
As you can see in this picture, the structure of any identifiers consist of
- The initial resolver service: domain which is unique and specific to each community e.g. ORCID for researchers
- Prefix: Unique number that represent category e.g. for DOI specific numbers refer to the publisher and directory
- Suffix: The unique dataset number and it is unique under its prefix
Exercise 1. Find the PID
From FAIRsharing, can you find the right database for protein dataset and explore its PID structure?
Solution
If you follow the steps in the following screen recording, you will find plant genomics and phenotypes. In this database, all datasets are assigned digital object identifier (DOI)
The DOI is a persisitent identifiers that follows the structure we explained before
Resources
The resources listed below provide an overview of the information you need to know about identifiers.
Unique and persistent identifiers: this link provide a nice and practical explanation of the unique and persistent identifiers > from FAIRCookbook
Identifiers: another nice explanation from RDMkit
Machine actionability: identifiers are also important for machine readability, a nice explanation from RDMkit that describes machine readability
Examples and explanation of different identifiers from FAIRsharing.org https://fairsharing.org/search? recordType=identifier_schema
Key Points
(Meta)data use a formal, accessible, shared, and broadly applicable language for knowledge representation (I1)
(Meta)data include qualified references to other (meta)data (A3)
Metadata are accessible, even when the data are no longer available (A2)