Metadata
Figure 1
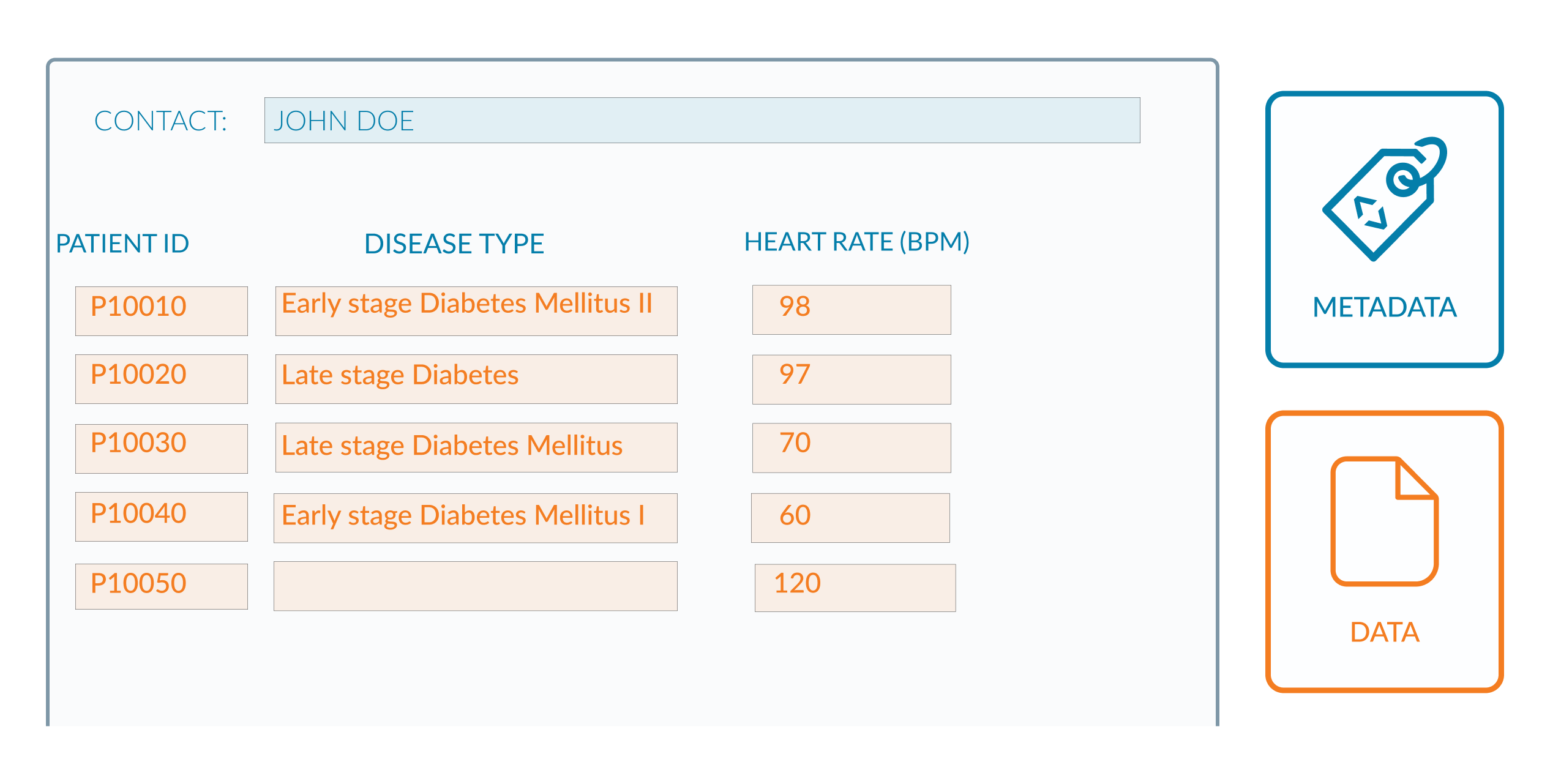
Figure 2
The column headings appear to be complete, though there are some issues with the data in orange. The diabetes status column appears to capture the disease’s type and stage. - In row 3, it is unclear whether the disease is Diabetes Mellitus or Diabetes Insipidus. - In row 4, it is unclear whether the type of diabetes mellitus is 1 or 2. - There is an empty space in the final row. It is unclear whether this is due to a lack of information or the patient does not have diabetes. So to do this better, two separate columns are created for the type and stage of the disease. The disease’s name included whether it was type 1 or type 2. You can check this in this figure 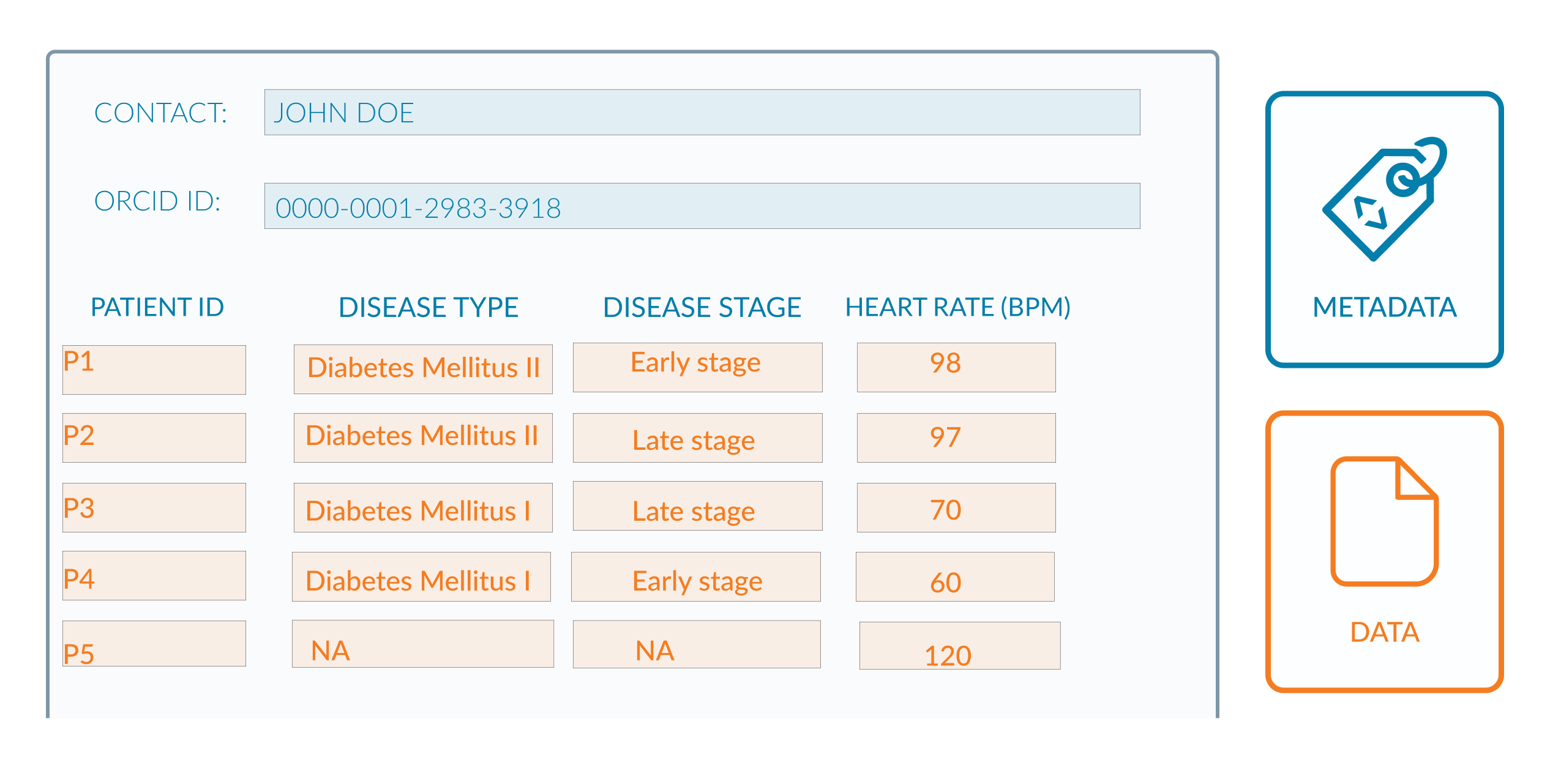
Figure 3
Let’s look at an example using microarray data from the arrayexpress database. This dataset contains data and metadata. The administrative metadata can be found in the orange square. The descriptive metadata is located in the black square, and as you can see, it summarize the dataset. The structure of dataset and files are marked by dark blue square which represents structural metadata. 
Figure 4
The building unit of FAIR cookbook is called a recipe, The recipe is the term used to describe instructions for how to FAIRify your data. As you see in the image, the structure of each recipe includes these main items: 1- Graphical overview which is the mindmap for the recipe 2- Ingredients which gives you an idea for the skills needed and tools you can use to apply the recipes 3- The steps and the process 4- Recommendations of what to read next and references to your reading 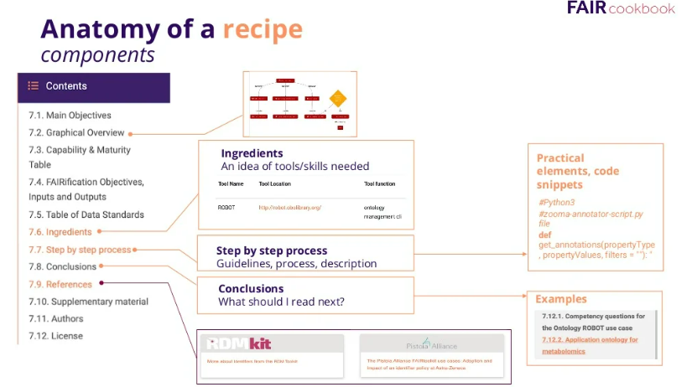
Figure 5
So let’s use the search box and write down metadata profiles  As you see the results comes up, choose metdata profiles. As we explained earlier the recipe shows necessary steps for creating metadata profiles for different data types
As you see the results comes up, choose metdata profiles. As we explained earlier the recipe shows necessary steps for creating metadata profiles for different data types
Figure 6
RDMkit is The Research Data Management toolkit for Life Sciences. It provides Best practices and guidelines to help you make your data FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable). It also provides catalogue of tools and resources for research data management.
Figure 7
As you can see in the above image, RDMkit covers a variety of research data management topics. The community standards are covered under domain tab. It provides community standards for all types of data.
Figure 8
4- Data publication and archiving
Figure 9
Figure 10
As you can see in this picture, you wil find data provenance in under protocol and experimental factors tab. 
Figure 11
 You can use the search wizard, to look for the guidelines for reporting the data and metadata of randomized controlled trials of the livestock and food.
You can use the search wizard, to look for the guidelines for reporting the data and metadata of randomized controlled trials of the livestock and food.
Figure 12
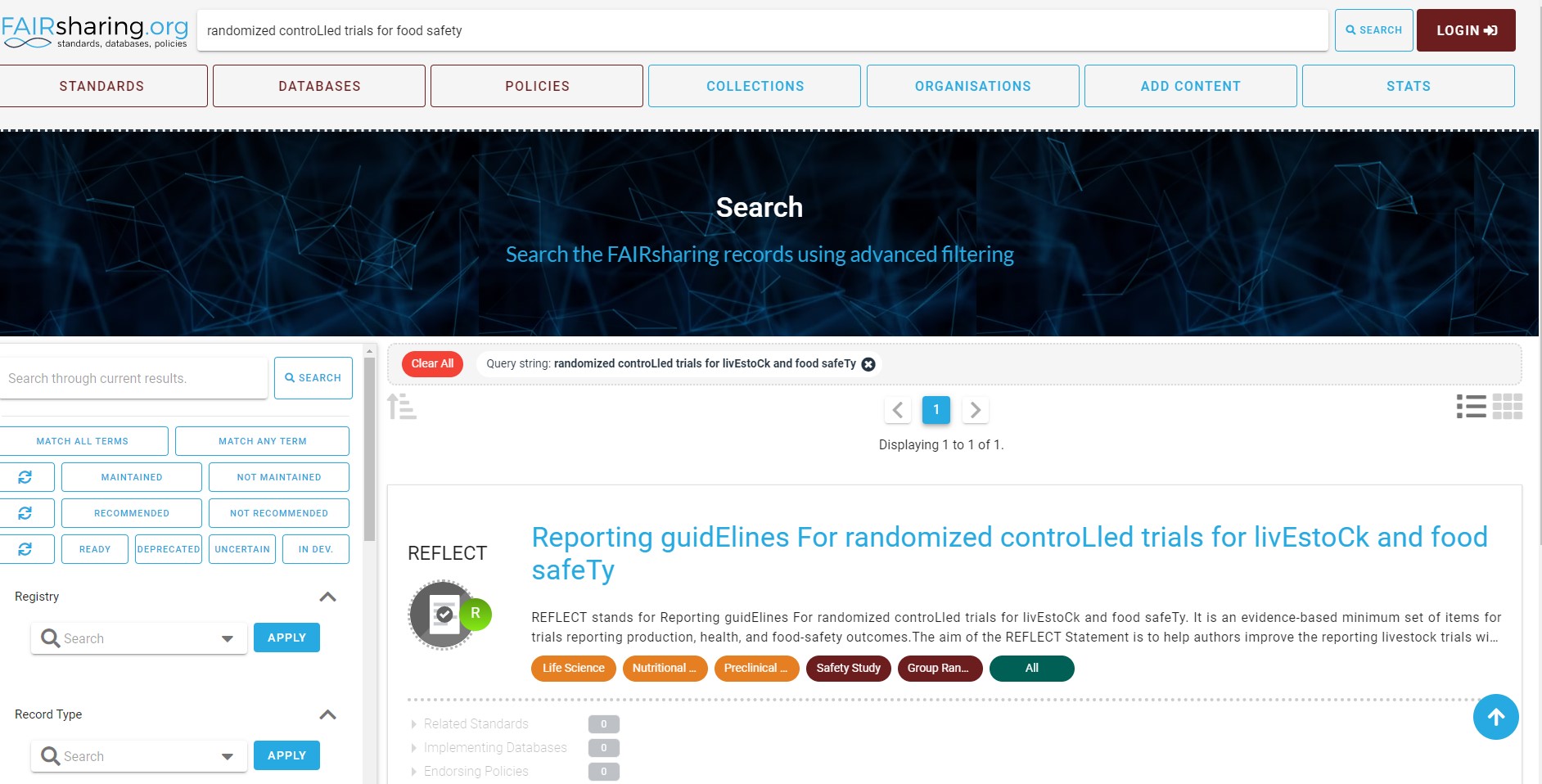 In the results section, you can find REFLECT guidelines.
In the results section, you can find REFLECT guidelines.
Figure 13
 For each resource/guideline, you will find general information, relationship graph, organization funding and maintaining the resource
For each resource/guideline, you will find general information, relationship graph, organization funding and maintaining the resource
Figure 14
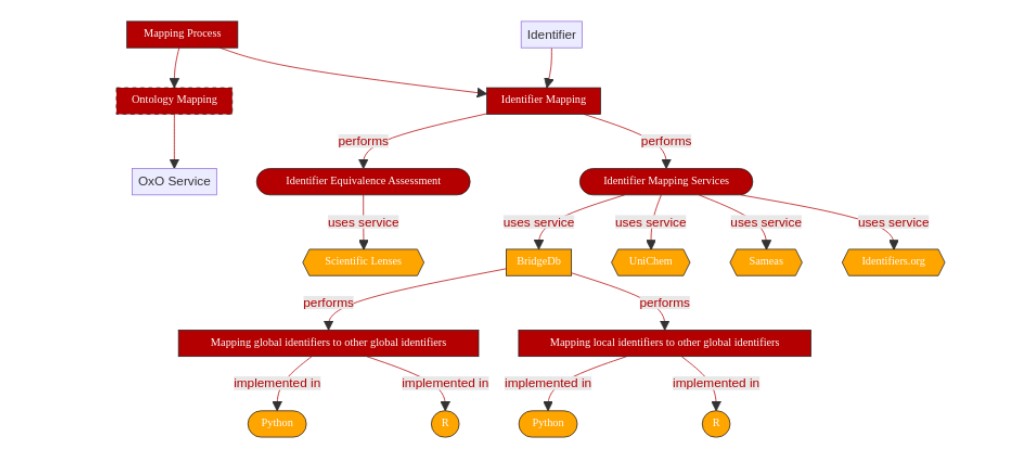
Identifiers
Figure 1
The PID in this case or as it called in array express “Accession” is E-MTAB-7933. If you use this accession number, you will find the dataset. In addition, have you noticed that also the data files are named using this PID .
Figure 2
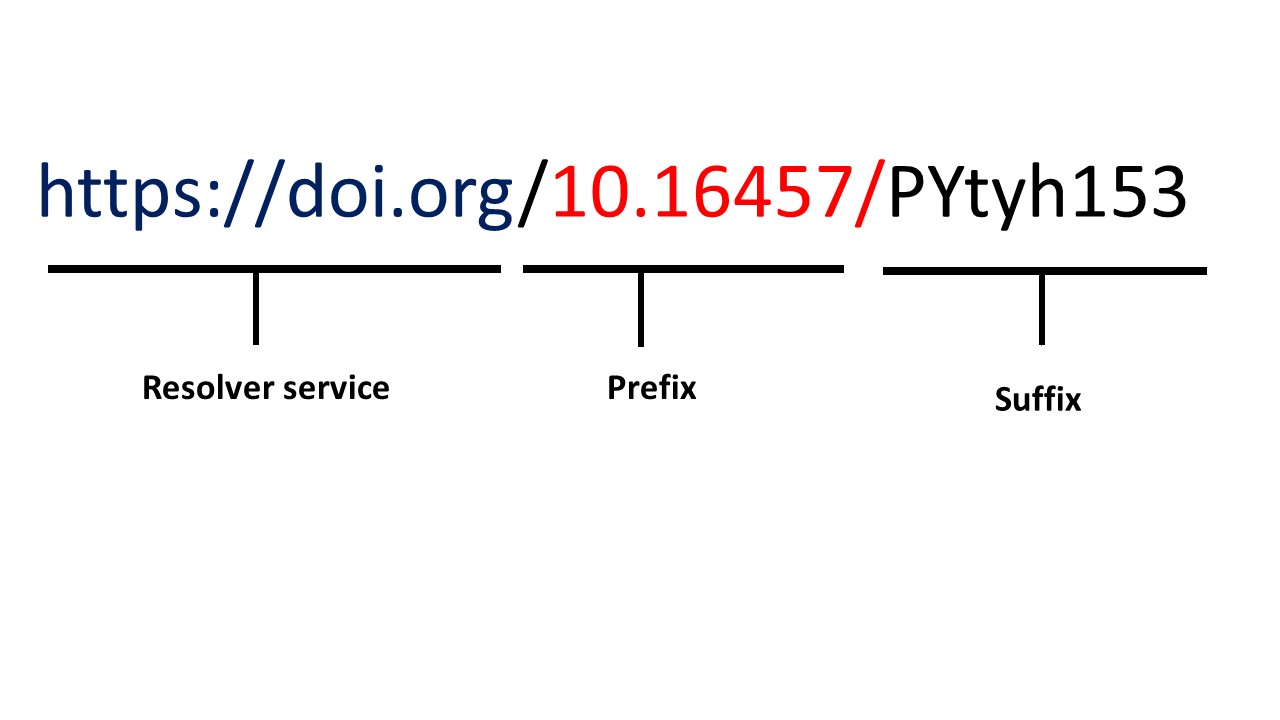
Access
Figure 1
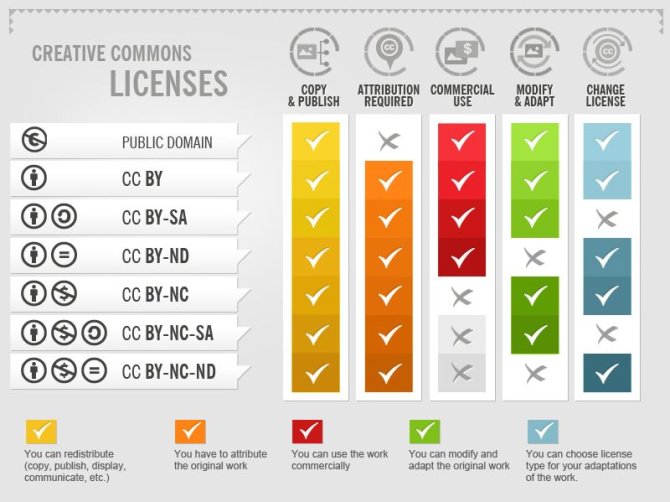
Figure 2
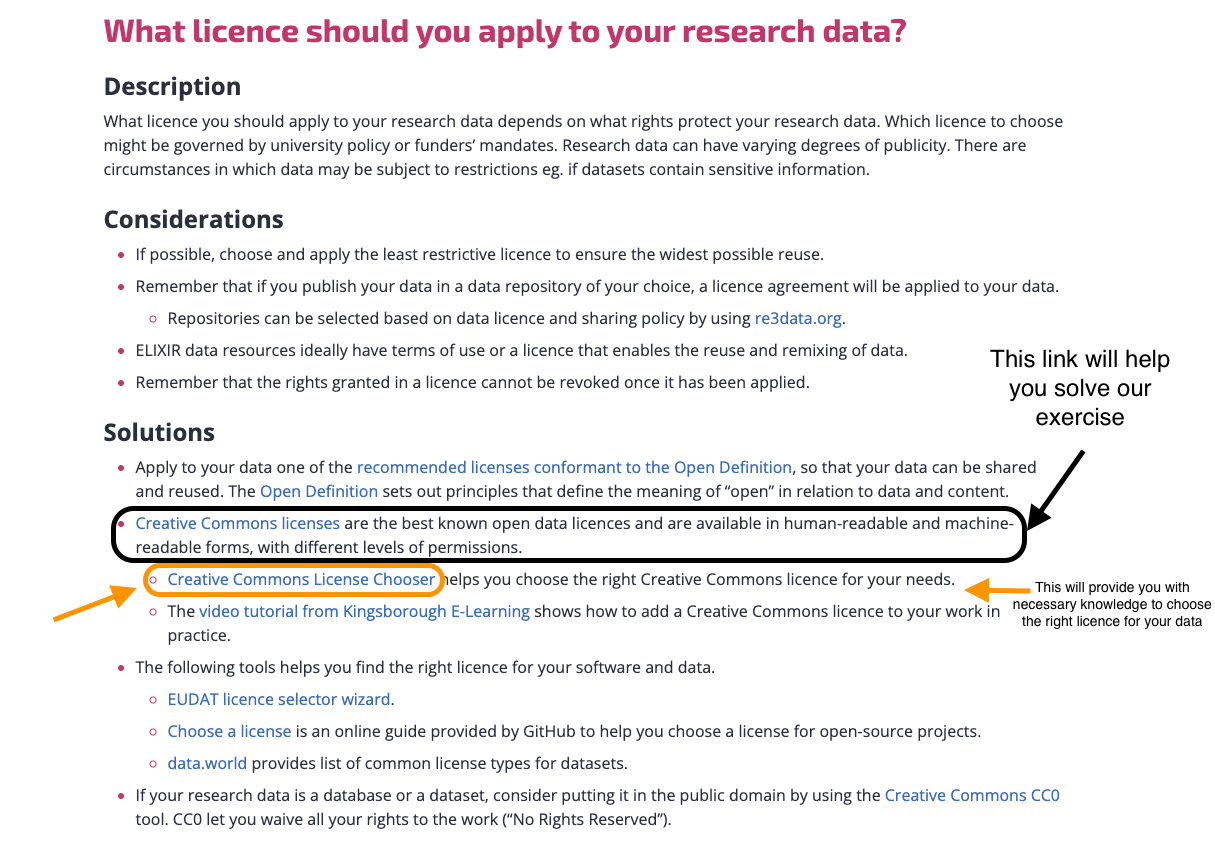 From this section, you can clearly understand the type of licence used for: 1- A large-scale COVID-19 Twitter chatter dataset for open scientific research - an international collaboration is CC-BY-4 2- RNA-seq of circadian timeseries sampling (LL2-3) of 13-14 day old Arabidopsis thaliana Col-0 (24 h to 68 h, sampled every 4 h) is CC-BY-4
From this section, you can clearly understand the type of licence used for: 1- A large-scale COVID-19 Twitter chatter dataset for open scientific research - an international collaboration is CC-BY-4 2- RNA-seq of circadian timeseries sampling (LL2-3) of 13-14 day old Arabidopsis thaliana Col-0 (24 h to 68 h, sampled every 4 h) is CC-BY-4Registration
Figure 1
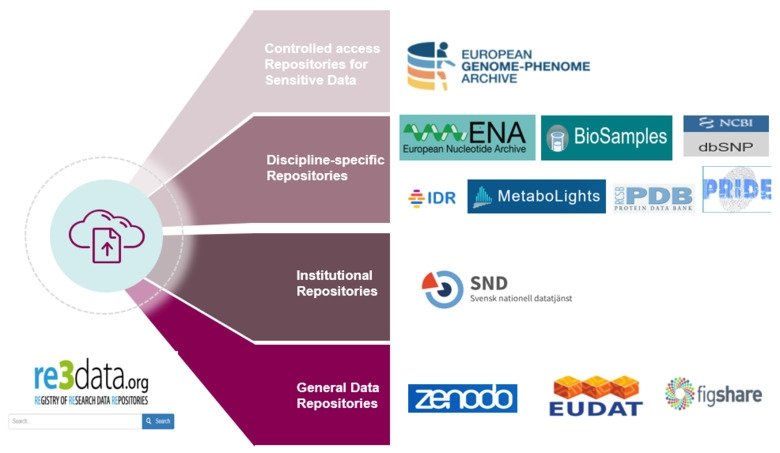
Figure 2
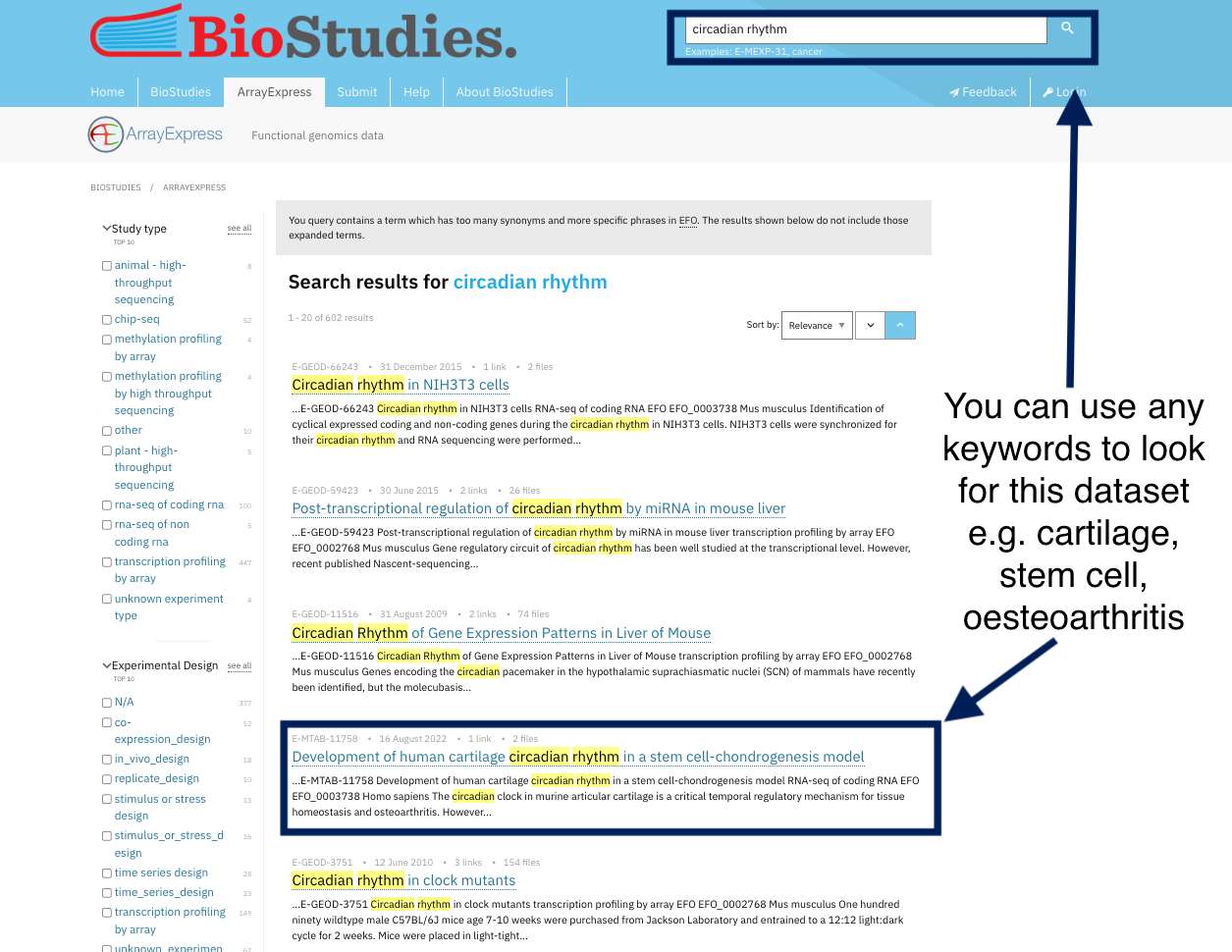
Figure 3
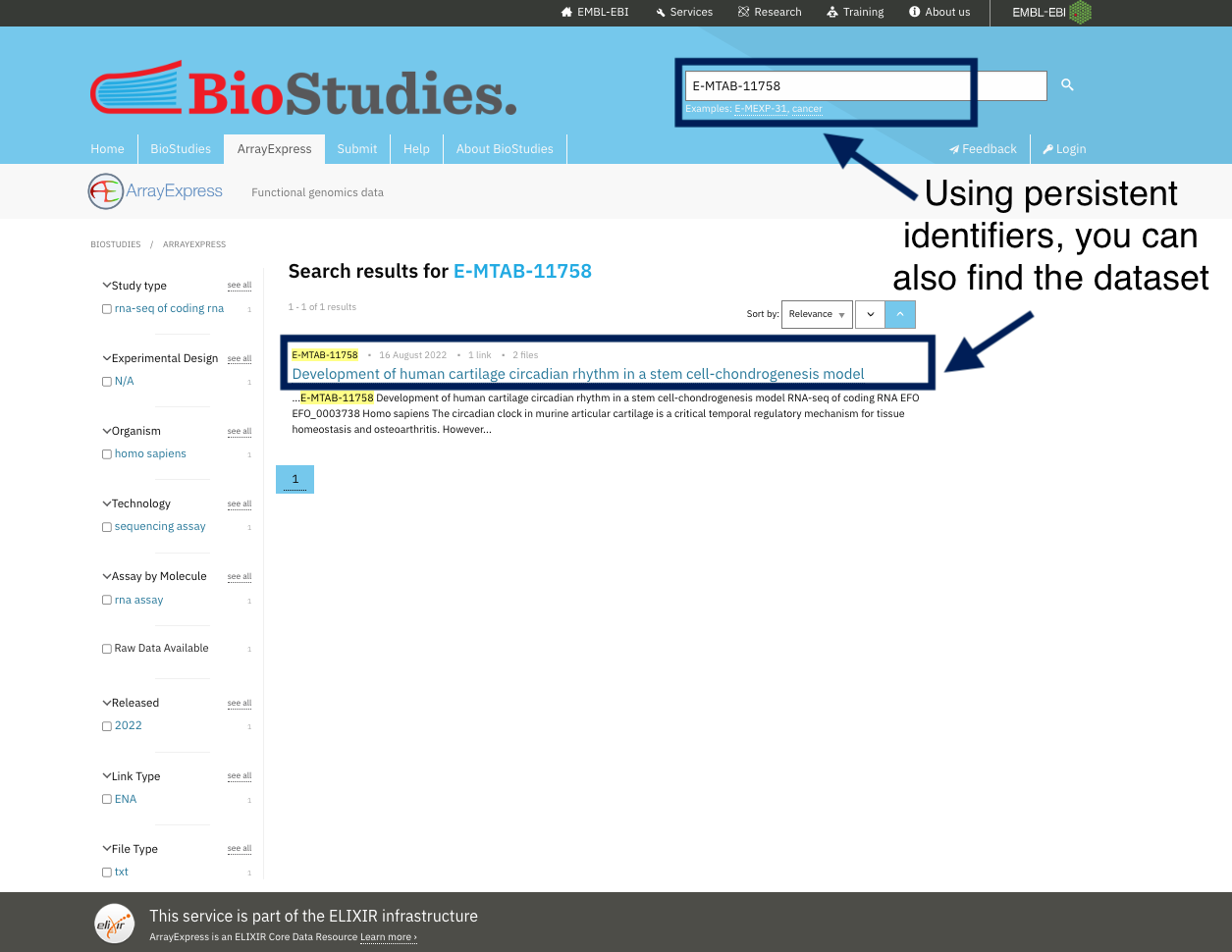
Figure 4
1- In this exercise, we are looking for a recipe on indexing or registering dataset in a searchable resource which you can find it in the findability tab, Can you find it in this picture? 
Figure 5
3- on the left side, you will find a navigation bar which will help you find different recipes that make your data findable. 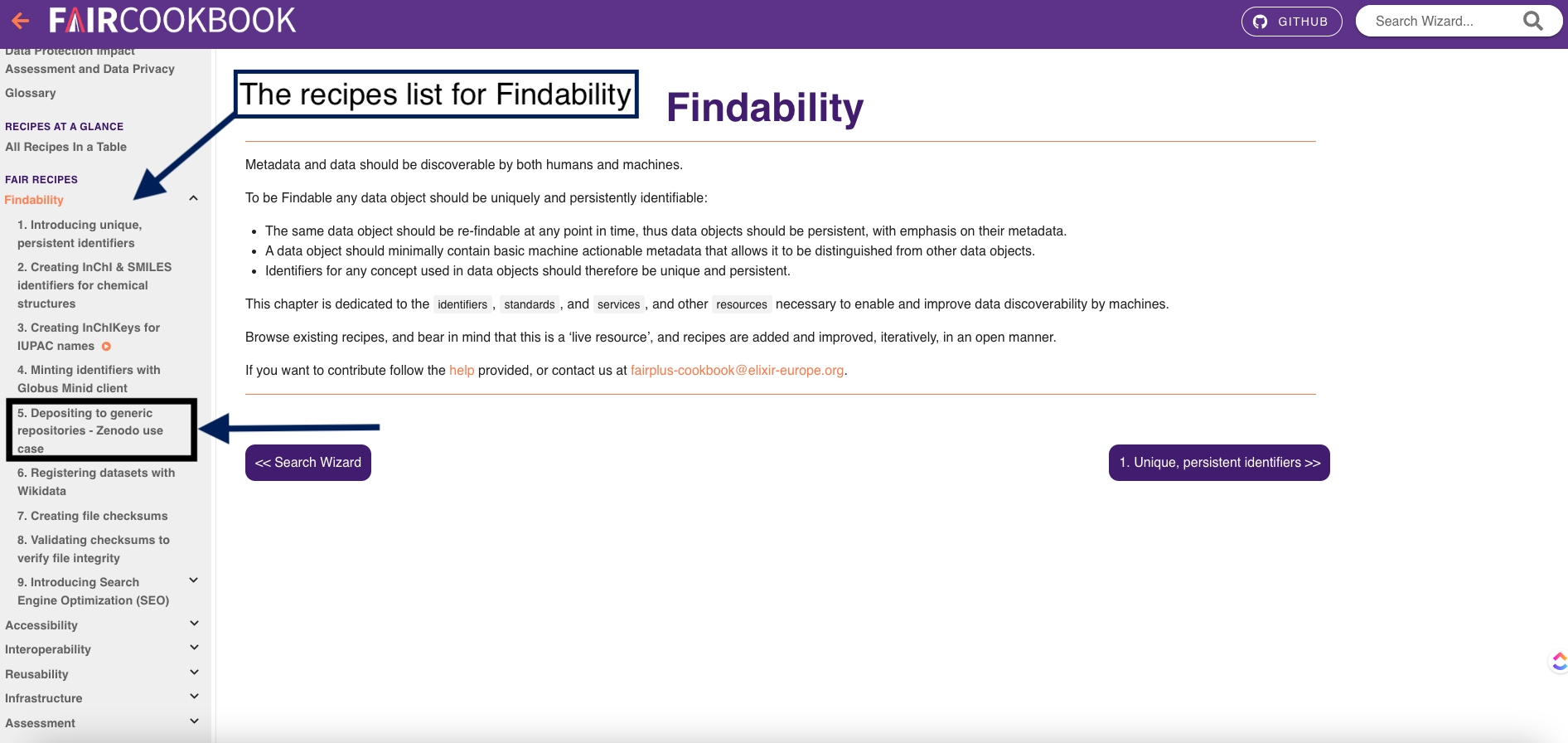
Figure 6

