Registration
Last updated on 2025-01-14 | Edit this page
Outcomes
1- Define what is data repository
2- Illustrate the importance of indexed data repository
3- Summarize the steps of data indexing in a searchable repository
Indexed data repository
what is a data repository?
It is a general term used to describe any storage space you use to deposit data, metadata and any associated research. Kindly note that database is more specific and it is mainly for the storage of your data.
Types of data repository
There are many types of data repsoitory classified based on:
1- The structure of the data: Data warehouse, Data lake and Data mart
The following table summarize these differences
| Data repository | Data warehouse | Data mart | Data lake |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supported data types | Structured | Highly Structured | Structured, semi-structured, unstructured, binary |
| Data quality | curated | Highly curated | Raw data |
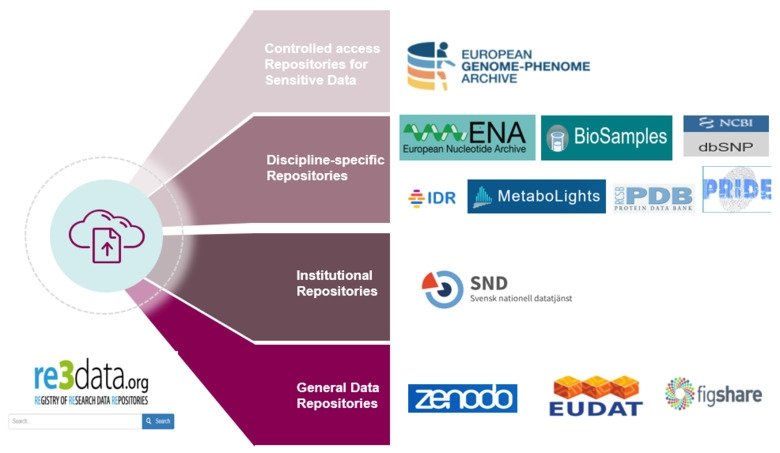
2- The purpose of data repository into:
Controlled access repository
Discipline specific repository
Institutional repository
General data repository
The following image summarize these types with different examples
Importance of indexed data repository
To ensure data findability, your data should be uploaded to a public repository where your data can be searched and found, It will make your data comply with the fourth principle of findability (F4) which states that . There are numerous databases where you can upload your data, these are typically data-driven. Examples of these databases are ArrayExpress for microarray data and RNAseq data. These databases have a set of rules in place to make sure that your data will be FAIR.
After you upload your data into this database, they are assigned an ID and are indexed in the database. So whenever you look for the ID, or even use a keyword for your data, you will find your data.
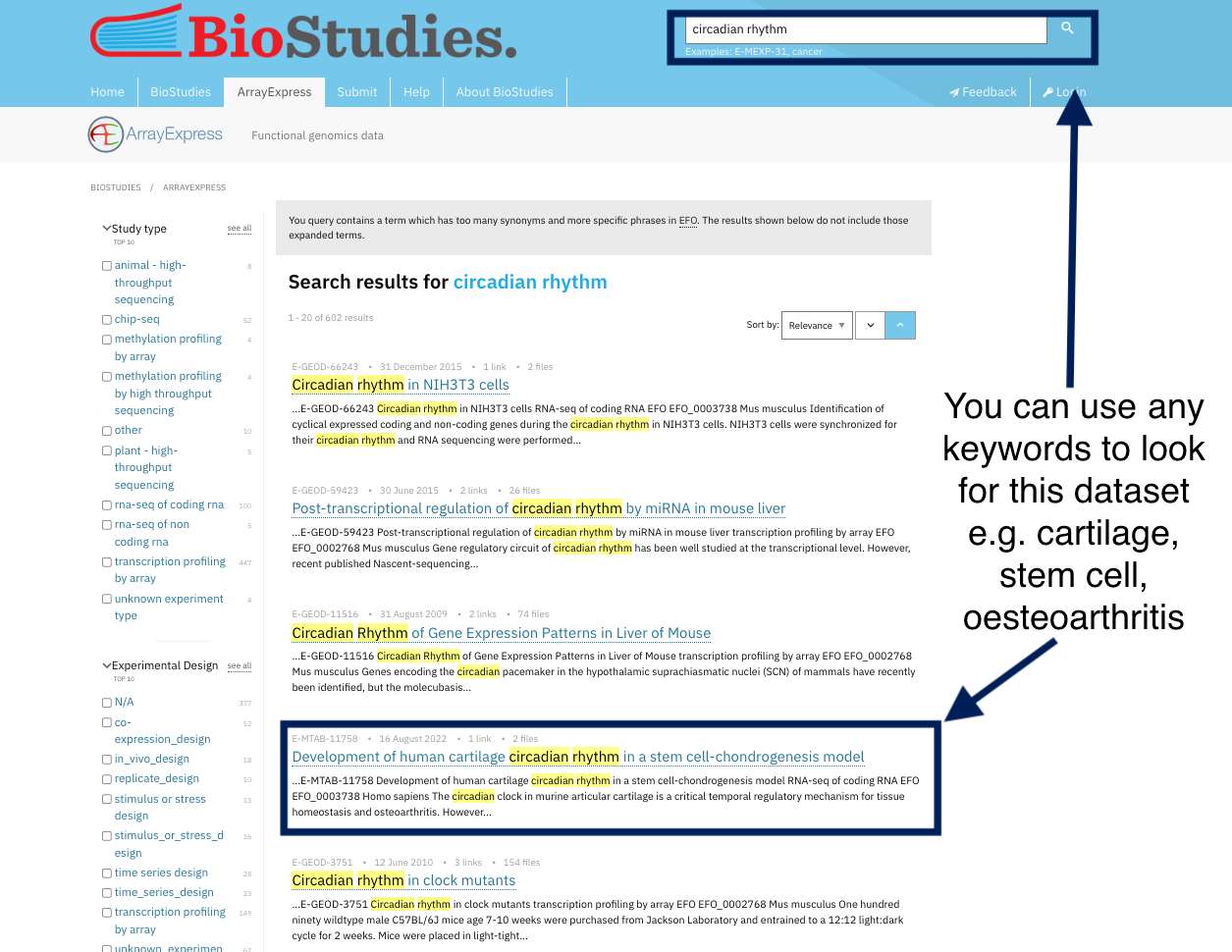
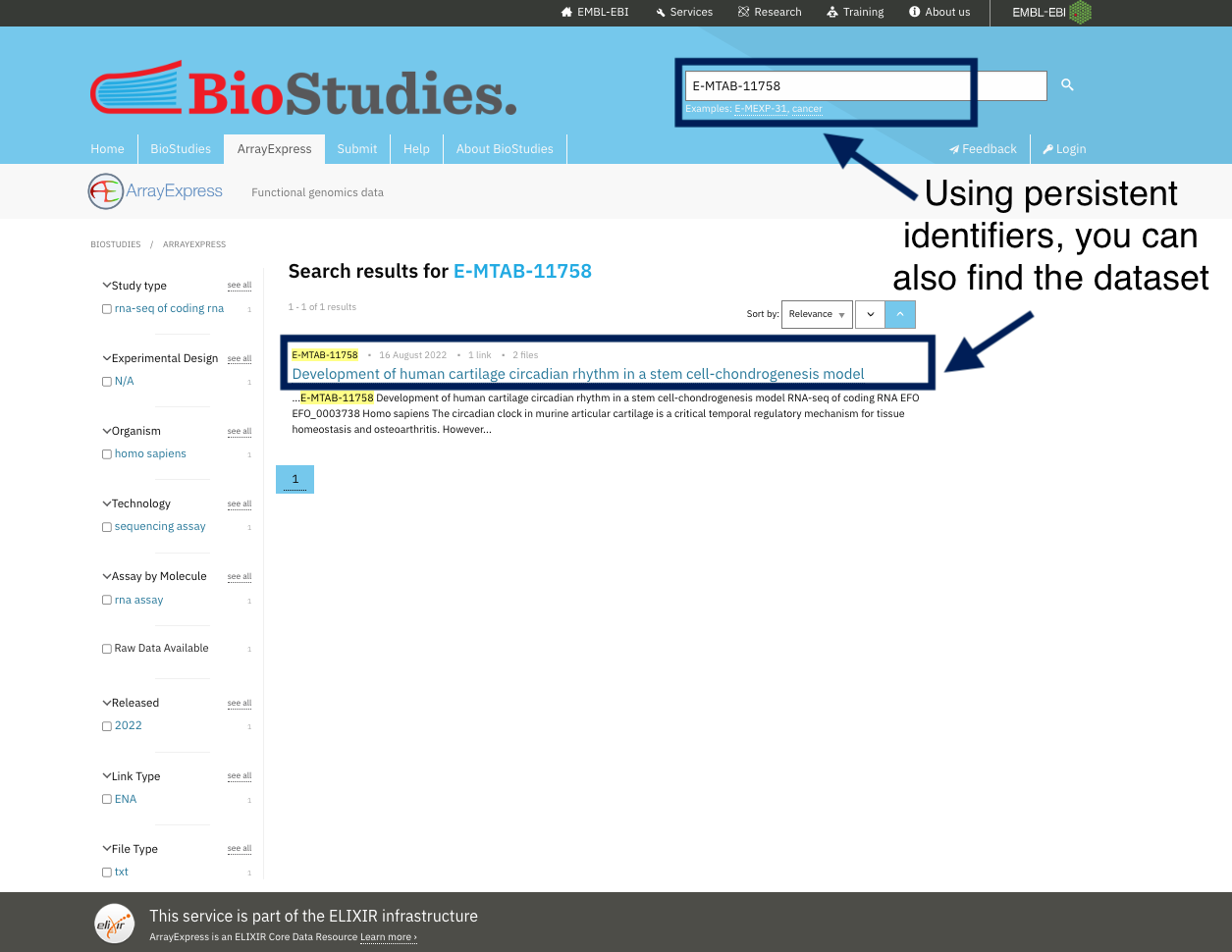
Take a look at the ArrayExpress database where all datasets are indexed, and you can simply find any dataset using the search tools. By indexing data, you can get the dataset using any keyword other than the PID. For example, if you want to locate human NSCL cell lines, you can just type this into the search toolbox and find the dataset. Indexing and registering datasets, also means they are curated in such a way that you may discover them using different keywords.
For example, you can find the same dataset by using its identifiers or by using keywords chosen by the dataset’s authors to describe it.
Exercise
One of the things you can do to index your dataset, is to upload it to Zenodo, can you use one of the resources we recommended before to know how to do this?
1- RDMkit
2- FAIRcookbook
3- FAIRsharing
Since you want a technical guideline, FAIRcookbook and RDMkit are the best to start with. We will start with FAIRcookbook As we explained before the structure of the recipe so let’s look for the suitable recipe in the FAIRcookbook So as you navigate the homepage of FAIRcookbook, you will find different tabs that covers each of FAIR principles, so for instance, if you want recipes on Accessibility of FAIR, you will find all recipes that can help you make your data accessible.
- Follow the following steps to find the recipe:
1- In this exercise, we are looking for a recipe on indexing or registering dataset in a searchable resource which you can find it in the findability tab, Can you find it in this picture? 
2- Click on the findability tab
3- on the left side, you will find a navigation bar which will help you find different recipes that make your data findable. 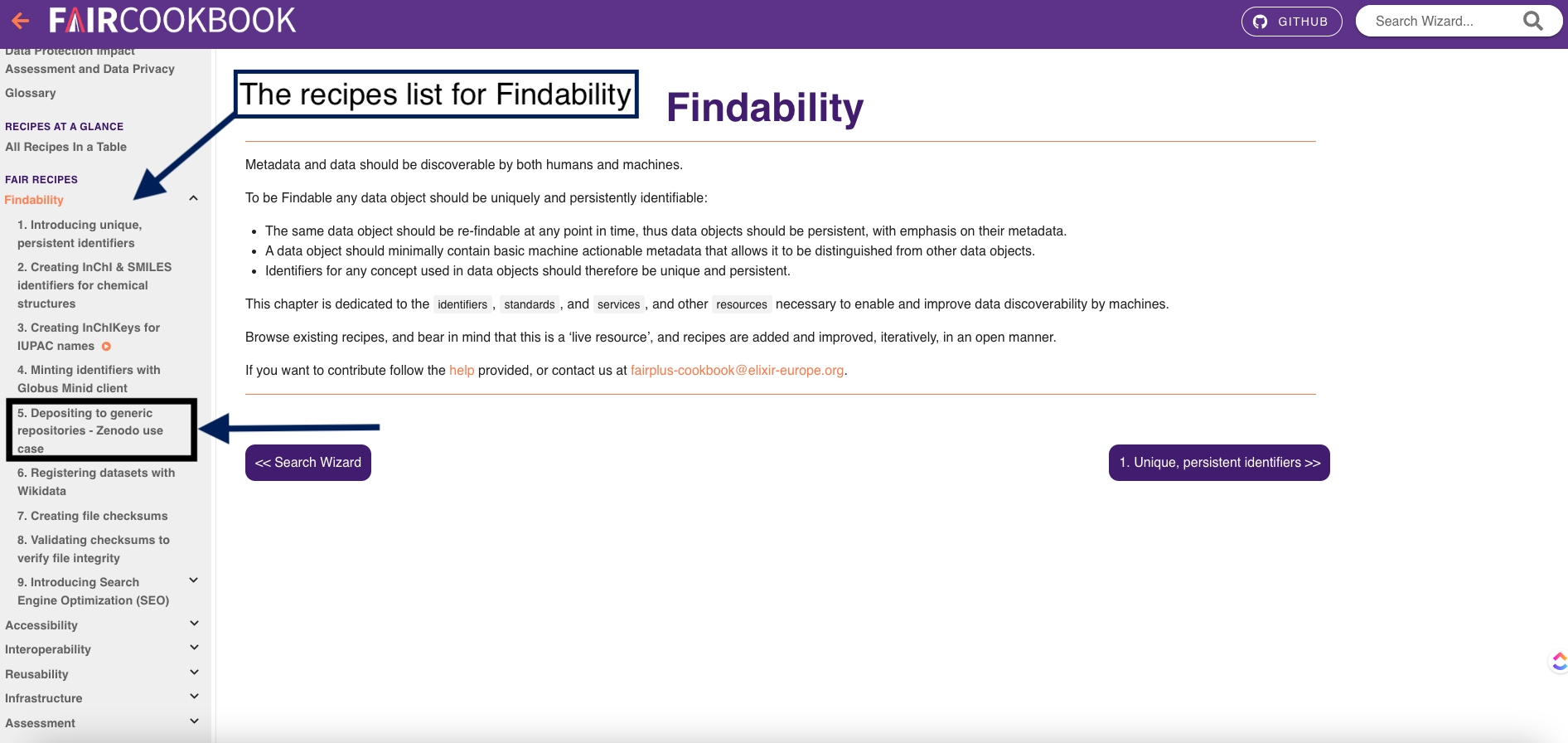
4- As you can see here, you will find a recipe on registering datasets with Wikidata and another one on depositing to generic repositories-Zenodo use case
Once you click on one of these resources, you will find the following:
- Requirements that you need to apply the recipe to your dataset
- The instructions
- References and further readings
- Authors and licence

In our specialized courses, we will give you examples on how to upload your data to specialized repository
Why should you upload your data to a database?
1- Databases assign your data a unique persistent identifier.
2- Your data will be indexed, making it easier to find.
3- Some databases will let you easily connect your dataset to other datasets.
4- Dataset licencing, with some databases offering controlled or limited access to protect your data.
By uploading data to a database, you comply with the following FAIR principles
F1 (Meta)data is assigned a globally unique and persistent identifier
F3 Metadata clearly and explicitly include the identifier of the data they describe
F4 (Meta)data is registered or indexed in a searchable resource
It will also allow your data to be more accessible as the standardized communications protocol and authentication are automatically set for your data
A1 (Meta)data is retrievable by their identifier using a standardised communications protocol
A1.1 The protocol is open, free, and universally implementable
A1.2 The protocol allows for an authentication and authorisation procedure, where necessary
A2 Metadata is accessible, even when the data is no longer available
I3 (Meta)data include qualified references to other (meta)data
R1.1 (Meta)data is released with a clear and accessible data usage license
How to choose the right database for your dataset?
1- Check the community standards for your data, you can find more information RDMkit guidelines on domain specific community standards
2- Look for resources that describe the databases and check if it fits your data, you might consider the following:
- Accessibility options
- Licence
One of these resources is FAIRsharing, it provides a registry for different databases and repositories. Here is an example where the FAIR sharing provides you with information regarding protein database. It has the following information
1- General information
2- Which policies use this database?
3- Related community standards
4- Organization maintaining this database
5- Documentation and support
6- Licence
Resources
Our resources provide an overview of data repositories and examples
The FAIR cookbook and RDMkit both provide excellent instructions for uploading your data into databases:
- FAIRcookbook recipe on Depositing to generic repositories- Zenodo use
- FAIRcookbook recipe on Registering Datasets in Wikidata
- RDMkit guidelines on Data publications and depostion
- RDMkit guidelines on Finding and reusing existing data
- FAIRcookbook recipe on Search engine optimization
- FAIRsharing offers a nice portal to different examples of databases
FAIR principles
This episode covers the following principles:
1- (F4) (meta)data are registered or indexed in a searchable resource
2- (R1.1) (Meta)data are released with a clear and accessible data usage license
